Ulcerative Colitis Surgery Specialist Q&A
Ulcerative colitis symptoms can vary in severity and may include abdominal pain, diarrhea, rectal bleeding, urgency to have a bowel movement, fatigue, weight loss, and fever. In severe cases, individuals may experience complications such as dehydration, anemia, and inflammation beyond the colon. Ulcerative Colitis Surgery is offered by Dr. Debora J. Fox-McClary, M.D., MBA, FACS, FASCRS, and her team at Phoenix Unified Surgeons. We are conveniently located at 20333 N 19th Avenue, Ste 230 Phoenix, AZ 85027. For more information, contact us or request an appointment online.


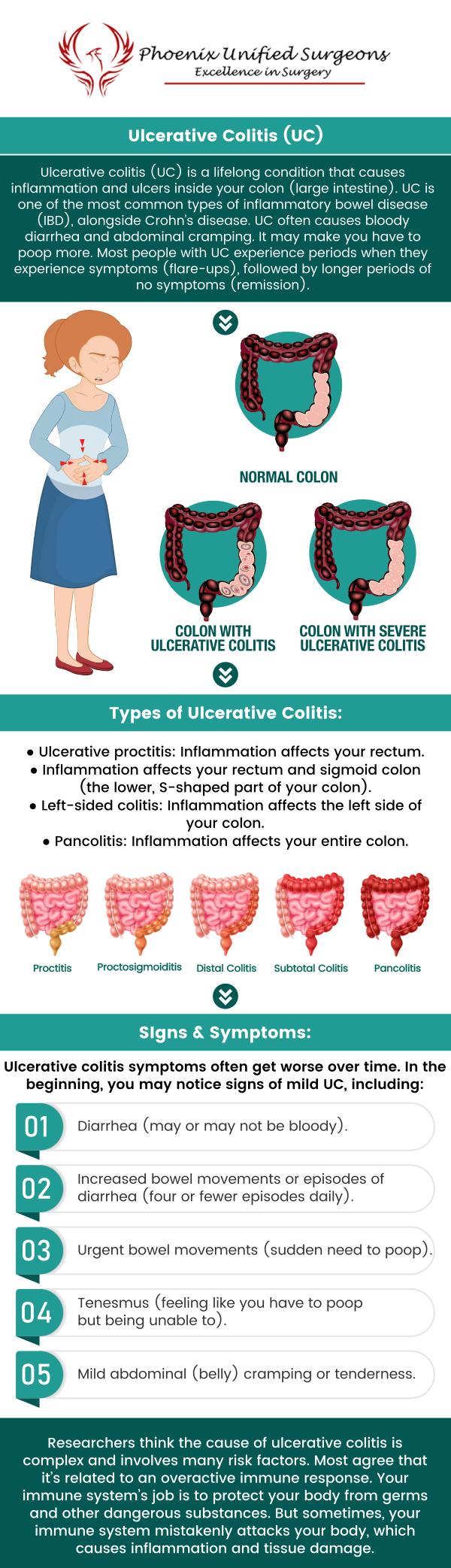
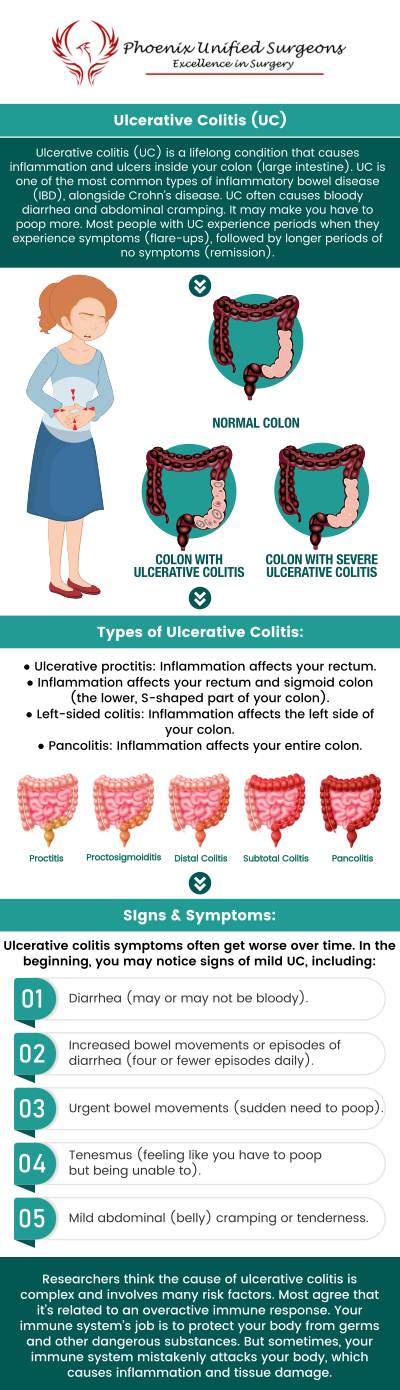
Table of Contents:
What is ulcerative colitis (UC)?
How common is ulcerative colitis?
What are the symptoms of ulcerative colitis?
How is ulcerative colitis diagnosed?
How is ulcerative colitis treated?
Ulcerative colitis, also referred to as UC, is one of the most common types of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), alongside Crohn’s disease. UC is characterized by the chronic inflammation of the colon and rectum, which can lead to a variety of uncomfortable and often debilitating symptoms.
Patients with this condition often experience episodes of bloody diarrhea and abdominal cramping. These flare-ups cause significant discomfort and have a negative impact on daily life. They may vary in severity and duration. The exact cause of UC is not fully understood; however, it is believed to involve a combination of immune system problems and other triggers, such as diet and stress.
Ulcerative colitis is relatively common. This condition affects about 1 million Americans. As a chronic inflammatory bowel disease, UC can significantly affect the daily lives of those who suffer from it, causing symptoms such as bloody diarrhea, abdominal cramping, and fatigue. UC can occur at any age but is often diagnosed in young adults between the ages of 15 and 35 as well as older adults aged 50 to 70.
Some of the symptoms of UC include:
• Bloody diarrhea – Some of the most characteristic signs of UC are diarrhea and rectal bleeding. This occurs because the inflammation in the colon causes small ulcers, which can bleed, leading to blood mixed with your stool.
• Abdominal pain and cramping – UC often causes abdominal discomfort and cramping, usually located in the lower abdomen. This pain can range from mild to severe and is often linked to bowel movements.
• Unexplained weight loss – If you’re losing weight without trying, it could be due to UC. The inflammation can affect your appetite and the absorption of nutrients, leading to unintentional weight loss.
• Urgency – A sudden and urgent need to pass stools is a common symptom of UC.
• Fever – During a flare-up, it’s not uncommon to experience a low-grade fever. This indicates that your body is trying to fight off the inflammation in your colon.
• Chronic fatigue – The constant inflammation and frequent trips to the bathroom can drain your energy, leaving you feeling constantly fatigued. Chronic tiredness can interfere with work, social activities, and your overall quality of life.
The only way to diagnose UC is through endoscopic procedures with a biopsy. While other diagnostic procedures, such as blood tests or stool samples, may be performed during the diagnosis, these tests are used to rule out other conditions that may be causing your symptoms, such as infections caused by parasites, bacteria, or viruses.
Healthcare professionals will perform a colonoscopy or a flexible sigmoidoscopy to get a clear view of your colon. During these procedures, a doctor uses a flexible tube with a camera to examine the inside of your colon and rectum. Small tissue samples (biopsies) are taken from the colon lining and analyzed for signs of inflammation and ulcers, which are signs of UC.
UC is primarily treated with medications, but surgery and cancer monitoring also play crucial roles in managing the disease. Medications are the first line of treatment and include anti-inflammatory drugs, such as aminosalicylates and corticosteroids, to reduce inflammation in the colon.
Alternatively, immunosuppressants and biologics may be prescribed to target the immune system and reduce flare-ups. For many people, these medications can effectively control the symptoms of UC.
In cases where medications do not provide sufficient relief, surgery may be necessary. The most common surgical approach for addressing UC is a proctocolectomy, which involves removing the colon and rectum. Furthermore, regular cancer monitoring is essential for people with UC, as they are at an increased risk of developing colorectal cancer.
Depending on the nature and severity of your symptoms, your doctor will create a personalized treatment plan for you. If surgery is recommended for you, the experts at Phoenix Unified Surgeons can assess your needs and outline the best treatment approaches for your circumstances. We are conveniently located at 20333 N 19th Avenue, Ste 230 Phoenix, AZ 85027. For more information, contact us or request an appointment online. We serve patients from Phoenix AZ, Sun City AZ, Peoria AZ, Surprise AZ, Glendale AZ, Scottsdale AZ, and surrounding areas.
Check Out Our 5 Star Reviews



Additional Services You May Need
▸ Colon & Rectal Surgery
▸ Gallbladder Surgery
▸ Colonoscopy
▸ Wound Care
▸ Hernia Repair
▸ General Surgery
▸ Robotic and Minimally Invasive Surgery
▸ Appendectomy
▸ Colon Repair/Resection
▸ Lipoma & Cyst Removal
▸ Endoscopy and Colonoscopy
▸ Abdominal Pain
▸ Colon surgery for Diverticulitis
▸ Colon surgery for Colon Cancer
▸ Hemorrhoids
▸ Anal Fistulas
▸ Anal Pain Surgeries
▸ Colostomy Avoidance Surgery
▸ Fecal Incontinence Surgery
▸ Crohn’s Surgery
▸ Ulcerative Colitis Surgery
▸ TIF Procedure






